Subjects were show an object and were later presented with a rotated version of the same object. The further the object was rotated from its initial position, the longer it took the subjects to decide if the figure was the same as the original one.
The subjects rotated images in their heads in much the same way that they would rotate physical objects in space.
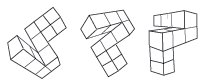
Conclusion: the mental image being rotated a spatial properties analogous to those of an object.
Stephen Kosslyn (1994).
Note: Kosslyn credits R.N. Shepherd, J. Metzler, and I.A. Cooper with earlier versions of this experiment.