|

| Boltzmann-Schuetz hypothesis Opinion1 #104155 Boltzmann and Schuetz claimed that in a universe that is near thermal equilibrium, and given sufficient time, there will be regions where there is a temporary deviation into a low entropy state, from which it will trend back to equilibrium. Anthropic selection accounts for us being in such a region. | Boltzmann suggested this explanation in a letter to Nature in 1895 - he attributes the idea 'to my old assistant Dr Schuetz'. The basic idea is depicted in the following diagram. The downward spikes represent low-entropy occurrences, with the system in the high entropy state most of the time. We are presumed to be at some position like A or B - the slope doesn't matter (case C is discussed elsewhere). 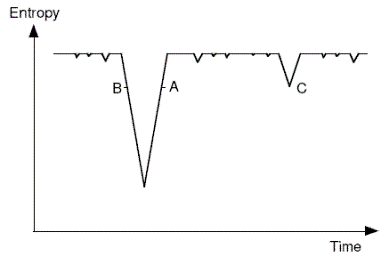 Note that in the passage cited below Boltzmann presumes that the thermodynamic arrow determines the psychological arrow of time. This issue is explored elsewhere in the map (follow cross-link). |
+Citations (3) - CitationsAjouter une citationList by: CiterankMapLink[1] Boltzmann-Schuetz hypothesis
En citant: Huw Price - Head of the Center for Time, University of Sydney
Cité par: Peter Baldwin 7:05 AM 15 April 2011 GMT
Citerank: (6) 100641The Arrow of Time?A map exploring some issues concerning the nature of time that lie at the boundary of physics and philosophy. The map follows up a talk to the Blackheath Philosophy Forum on 2 April 2011 by Huw Price, Professor of Philosophy and director of the Center for Time at Sydney University.7F1CEB7, 103807The experience of timeThis branch of the map considers the phenomenology of time - the various ways in which time presents itself directly to our consciousness. Why do we think time has the features indicated by the passage view? The answers will hopefully enable us to connect the phenomenological to the physical.8FFB597, 103810Why do we see an entropy gradient?We find ourselves in an observable universe in which entropy increases consistently in one direction, thereby showing time asymmetry - an arrow of time. Yet the vast majority of underlying dynamical processes are time-symmetric. How to account for this? Two broad approaches are considered here.8FFB597, 103810Why do we see an entropy gradient?We find ourselves in an observable universe in which entropy increases consistently in one direction, thereby showing time asymmetry - an arrow of time. Yet the vast majority of underlying dynamical processes are time-symmetric. How to account for this? Two broad approaches are considered here.8FFB597, 104152Past hypothesisWe inhabit a universe - or part thereof - characterized by a low-entropy past that has enabled the evolution of intelligent observers to occur. This together with Boltzmann's probabilistic argument (see sibling node) implies entropy will increase over time toward thermal equilibrium.109FDEF6, 105365Anti-matter objectionIf the time-asymmetry of thermodynamics were associated with the symmetry violation of the neutral K meson (neutral Kaon) then anti-matter would show the reverse of the normal thermodynamic asymmetry AND no such anti-matter reversal is apparent.13EF597B
URL: | | Extrait - "If the one-asymmetry view is correct, the puzzle of the thermodynamic arrow is really the puzzle of the low entropy boundary condition. Why is entropy so low in the past ? After all, in making it unmysterious why entropy doesn't decrease in one direction, the Boltzmann measure equally makes it mysterious why it does decrease in the other - for the statistics themselves are time symmetric.
Boltzmann himself was one of the �first to see the importance of this issue. In a letter to Nature in 1895, he suggests an explanation, based on an idea he attributes to `my old assistant, Dr Schuetz'. He notes that although low entropy states are very unlikely, they are very likely to occur eventually, given enough time. If the universe is very old, it will have had time to produce the kind of low entropy region we �nd ourselves inhabiting simply by accident. `Assuming the universe great enough, the probability that such a small part of it as our world should be in its present state, is no longer small,' as Boltzmann puts it.
It is one thing to explain why the universe contains regions like ours, another to explain why we fi�nd ourselves in such a region. If they are so rare, isn't it more likely that we'd �find ourselves somewhere else ? But Boltzmann suggests an answer to this, too. Suppose, as seems plausible, that creatures like us couldn't exist in the vast regions of near-equilibrium between such regions of low entropy. Then it's no surprise that we find ourselves in such an unlikely place." |
Link[2] Boltzmann's Anthropic Brain
En citant: Sean M. Carroll - Senior Research Associate, Department of Physics, Caltech
Publication date: 1 August 2006
Publication info: Discovery Magazine
Cité par: Peter Baldwin 7:12 AM 15 April 2011 GMT
Citerank: (3) 104151Boltzmann's statistical imperativeBoltzmann provided a statistical argument to show that an isolated system not at maximal entropy will is overwhelmingly likely to evolve toward higher entropy - hence the second law and the thermodynamic arrow.109FDEF6, 104158Boltzmann's Brain objectionGiven that the probability of low entropy states diminishes exponentially, we would expect to find ourselves in the minimum entropy fluctuation consistent with conscious experience. This would not be the appearance of a whole universe - just a minimal 'Boltzmann brain'.13EF597B, 114699Conscious observer requirement Conscious observers can only exist in an environment capable of evolving complex life, which requires the dissipation of free energy. This cannot occur in a condition at or near thermodynamic equilibrium. Hence observers like us will only be found in regions of the multiverse far from equilibrium.109FDEF6
URL:
| | Extrait - "Faced with the deep puzzle of why the early universe had a low entropy, Boltzmann hit on the bright idea of taking advantage of the statistical nature of the Second Law. Instead of a box of gas, think of the whole universe. Imagine that it is in thermal equilibrium, the state in which the entropy is as large as possible. By construction the entropy can’t possibly increase, but it will tend to fluctuate, every so often diminishing just a bit and then returning to its maximum. We can even calculate how likely the fluctuations are; larger downward fluctuations of the entropy are much (exponentially) less likely than smaller ones. But eventually every kind of fluctuation will happen.
You can see where this is going: maybe our universe is in the midst of a fluctuation away from its typical state of equilibrium. The low entropy of the early universe, in other words, might just be a statistical accident, the kind of thing that happens every now and then." |
Link[3] Zermelo's Second Objection - On the Mechanical Explanation of Irreversible Processes
En citant: Boltzmann, Ludwig
Cité par: Peter Baldwin 1:31 AM 5 August 2011 GMT
Citerank: (1) 115215Nothing specialOne hypothesis is that being in a down-entropy fluctuation will not seem special because the thermodynamic and psychological arrows are aligned. Some like Boltzmann (see citation) appear to have just assumed this. Others have tried to show it formally (follow cross-link).959C6EF
URL:
| | Extrait - SUMMARY
The second law of thermodynamics can be proved from the mechanical theory if one assumes that the present state of the universe, or at least that part which surrounds us, started to evolve from an improbable state and is still in a relatively improbable state. This is a reasonable assumption to make, since it enables us to explain the facts of experience, and one should not expect to be able to deduce it from anything more fundamental.
The applicability of probability theory to physical situations, which is disputed by Zermelo, cannot by rigorously proved, but the fact that one never observes those events that theoretically should be quite rare is certainly not a valid argument against the theory.
One may speculate that the universe as a whole is in thermal equilibrium and therefore dead, but there will be local deviations from equilibrium which may last for the relatively short time of a few eons. For the universe as a whole, there is no distinction between the "backwards" and "forwards" directions of time, but for the worlds on which living beings exist, and which are therefore in relatively improbable states, the direction of time will be determined by the direction of increasing entropy, proceeding from less to more probable states. |
|
|