t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE) is a machine learning algorithm for dimensionality reduction developed by Laurens van der Maaten and Geoffrey Hinton.[1] It is a nonlinear dimensionality reduction technique that is particularly well suited for embedding high-dimensional data into a space of two or three dimensions, which can then be visualized in a scatter plot. Specifically, it models each high-dimensional object by a two- or three-dimensional point in such a way that similar objects are modeled by nearby points and dissimilar objects are modeled by distant points.
The t-SNE algorithms comprises two main stages. First, t-SNE constructs a probability distribution over pairs of high-dimensional objects in such a way that similar objects have a high probability of being picked, whilst dissimilar points have an infinitesimalprobability of being picked. Second, t-SNE defines a similar probability distribution over the points in the low-dimensional map, and it minimizes the Kullback-Leibler divergence between the two distributions with respect to the locations of the points in the map.
t-SNE has been used in a wide range of applications, including computer security research,[2] music analysis,[3] cancer research,[4] and bio-informatics.[5]
Details[edit]
Given a set of 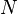 high-dimensional objects
high-dimensional objects 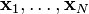 , t-SNE first computes probabilities
, t-SNE first computes probabilities 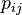 that are proportional to the similarity of objects
that are proportional to the similarity of objects  and
and  , as follows:
, as follows:

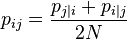
The bandwidth of the Gaussian kernels  , is set in such a way that the perplexity of the conditional distribution equals a predefined perplexity using a binary search. As a result, the bandwidth is adapted to the density of the data: smaller values of
, is set in such a way that the perplexity of the conditional distribution equals a predefined perplexity using a binary search. As a result, the bandwidth is adapted to the density of the data: smaller values of  are used in denser parts of the data space.
are used in denser parts of the data space.
t-SNE aims to learn a  -dimensional map
-dimensional map  (with
(with  ) that reflects the similarities
) that reflects the similarities 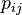 as good as possible. To this end, it measures similarities
as good as possible. To this end, it measures similarities 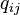 between two points in the map
between two points in the map  and
and 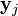 , using a very similar approach. Specifically,
, using a very similar approach. Specifically, 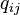 is defined as:
is defined as:

Herein a heavy-tailed Student-t distribution is used to measure similarities between low-dimensional points in order to allow dissimilar objects to be modeled far apart in the map CITATION.
The locations of the points  in the map are determined by minimizing the Kullback-Leibler divergence between the two distributions
in the map are determined by minimizing the Kullback-Leibler divergence between the two distributions  and
and 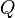 :
:
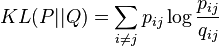
The minimization of the Kullback-Leibler divergence with respect to the points  is performed using gradient descent. The result of this optimization is a map that reflects the similarities between the high-dimensional inputs well.
is performed using gradient descent. The result of this optimization is a map that reflects the similarities between the high-dimensional inputs well.
References[edit]
- Jump up^ van der Maaten, L.J.P.; Hinton, G.E. (Nov 2008). "Visualizing High-Dimensional Data Using t-SNE". Journal of Machine Learning Research 9: 2579–2605.
- Jump up^ Gashi, I.; Stankovic, V., Leita, C., Thonnard, O. (2009). "An Experimental Study of Diversity with Off-the-shelf AntiVirus Engines". Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Network Computing and Applications: 4–11.
- Jump up^ Hamel, P.; Eck, D. (2010). "Learning Features from Music Audio with Deep Belief Networks". Proceedings of the International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference: 339–344.
- Jump up^ Jamieson, A.R.; Giger, M.L., Drukker, K., Lui, H., Yuan, Y., Bhooshan, N. (2010). "Exploring Nonlinear Feature Space Dimension Reduction and Data Representation in Breast CADx with Laplacian Eigenmaps and t-SNE". Medical Physics 37(1) 37: 339–351.doi:10.1118/1.3267037.
- Jump up^ Wallach, I.; Liliean, R. (2009). "The Protein-Small-Molecule Database, A Non-Redundant Structural Resource for the Analysis of Protein-Ligand Binding". Bioinformatics 25(5) 25 (5): 615–620. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp035.