Localized Epidemiological Agent-Based Simulation (ABS)
This ABS provides information about risk and the effects of both pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions, as well as detailed control over the rapidly evolving epidemiological characteristics of COVID-19. [1]
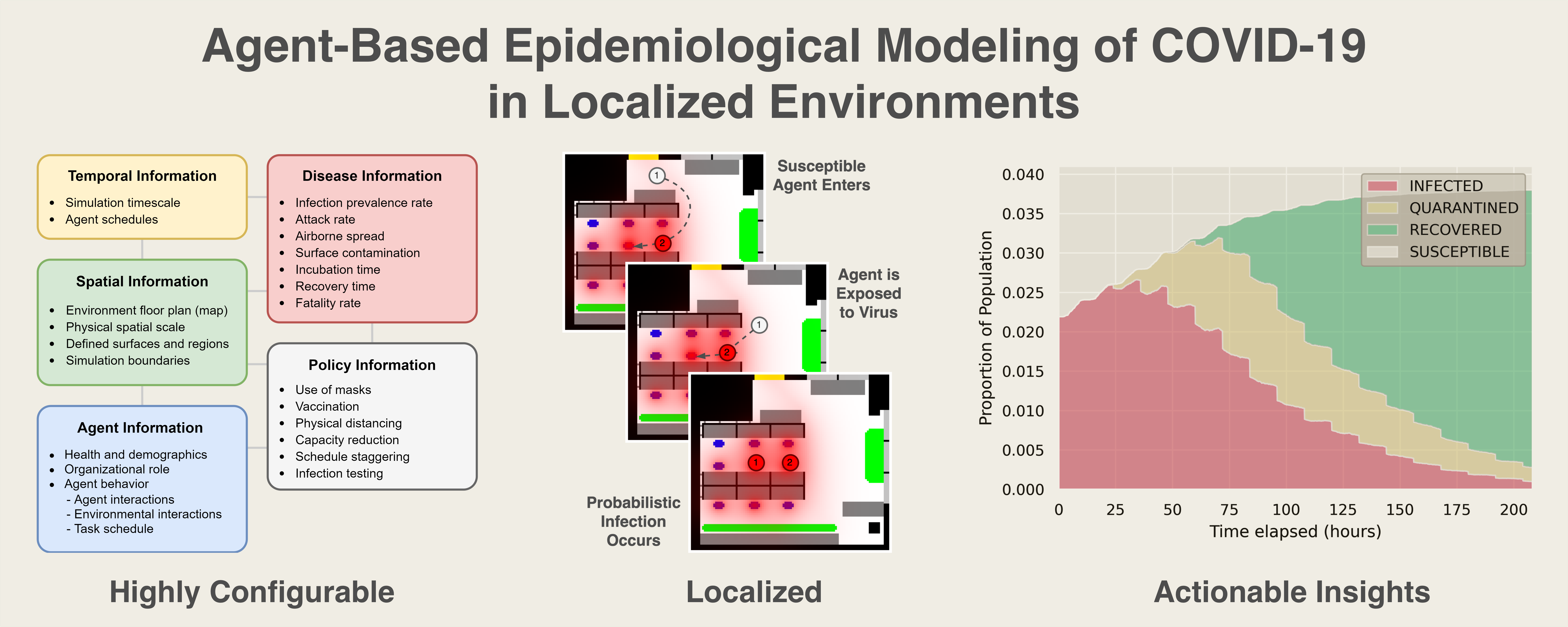
- Epidemiological modeling is used, under certain assumptions, to represent the spread of a disease within a population. Information generated by these models can then be applied to inform public health practices and mitigate risk. To provide useful and actionable preparedness information to administrators and policy makers, epidemiological models must be formulated to model highly localized environments such as office buildings, campuses, or long-term care facilities. In this paper, a highly configurable agent-based simulation (ABS) framework designed for localized environments is proposed.
- This ABS provides information about risk and the effects of both pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions, as well as detailed control over the rapidly evolving epidemiological characteristics of COVID-19. Simulation results can inform decisions made by facility administrators and be used as inputs for a complementary decision support system. The application of our ABS to our research lab environment as a proof of concept demonstrates the configurability and insights achievable with this form of modeling, with future work focused on extensibility and integration with decision support.