A recurrent neural network (RNN) is a class of neural network where connections between units form a directed cycle. This creates an internal state of the network which allows it to exhibit dynamic temporal behavior. Unlike feedforward neural networks, RNNs can use their internal memory to process arbitrary sequences of inputs. This makes them applicable to tasks such as unsegmented connected handwriting recognition, where they have achieved the best known results.[1]
Contents
[hide] - 1 Architectures
- 1.1 Fully recurrent network
- 1.2 Hopfield network
- 1.3 Elman networks and Jordan networks
- 1.4 Echo state network
- 1.5 Long short term memory network
- 1.6 Bi-directional RNN
- 1.7 Continuous-time RNN
- 1.8 Hierarchical RNN
- 1.9 Recurrent multilayer perceptron
- 1.10 Second Order Recurrent Neural Network
- 1.11 Pollack’s sequential cascaded networks
- 2 Training
- 2.1 Gradient descent
- 2.2 Global optimization methods
- 3 Related fields
- 4 Issues with recurrent neural networks
- 5 References
- 6 External links
Architectures[edit]
Fully recurrent network[edit]
This is the basic architecture developed in the 1980s: a network of neuron-like units, each with a directed connection to every other unit. Each unit has a time-varying real-valued activation. Each connection has a modifiable real-valued weight. Some of the nodes are called input nodes, some output nodes, the rest hidden nodes. Most architectures below are special cases.
For supervised learning in discrete time settings, training sequences of real-valued input vectors become sequences of activations of the input nodes, one input vector at a time. At any given time step, each non-input unit computes its current activation as a nonlinear function of the weighted sum of the activations of all units from which it receives connections. There may be teacher-given target activations for some of the output units at certain time steps. For example, if the input sequence is a speech signal corresponding to a spoken digit, the final target output at the end of the sequence may be a label classifying the digit. For each sequence, its error is the sum of the deviations of all target signals from the corresponding activations computed by the network. For a training set of numerous sequences, the total error is the sum of the errors of all individual sequences. Algorithms for minimizing this error are mentioned in the section on training algorithms below.
In reinforcement learning settings, there is no teacher providing target signals for the RNN, instead a fitness function or reward function is occasionally used to evaluate the RNN's performance, which is influencing its input stream through output units connected to actuators affecting the environment. Again, compare the section on training algorithms below.
Hopfield network[edit]
The Hopfield network is of historic interest although it is not a general RNN, as it is not designed to process sequences of patterns. Instead it requires stationary inputs. It is a RNN in which all connections are symmetric. Invented by John Hopfield in 1982, it guarantees that its dynamics will converge. If the connections are trained using Hebbian learning then the Hopfield network can perform as robust content-addressable memory, resistant to connection alteration.
A variation on the Hopfield network is the bidirectional associative memory (BAM). The BAM has two layers, either of which can be driven as an input, to recall an association and produce an output on the other layer.[2]
Elman networks and Jordan networks[edit]
The following special case of the basic architecture above was employed by Jeff Elman. A three-layer network is used (arranged vertically as x, y, and z in the illustration), with the addition of a set of "context units" (uin the illustration). There are connections from the middle (hidden) layer to these context units fixed with a weight of one.[3] At each time step, the input is propagated in a standard feed-forward fashion, and then a learning rule is applied. The fixed back connections result in the context units always maintaining a copy of the previous values of the hidden units (since they propagate over the connections before the learning rule is applied). Thus the network can maintain a sort of state, allowing it to perform such tasks as sequence-prediction that are beyond the power of a standard multilayer perceptron.
Jordan networks, due to Michael I. Jordan, are similar to Elman networks. The context units are however fed from the output layer instead of the hidden layer. The context units in a Jordan network are also referred to as the state layer, and have a recurrent connection to themselves with no other nodes on this connection.[3] Elman and Jordan networks are also known as "simple recurrent networks" (SRN).
Echo state network[edit]
The echo state network (ESN) is a recurrent neural network with a sparsely connected random hidden layer. The weights of output neurons are the only part of the network that can change and be trained. ESN are good at reproducing certain time series.[4] A variant for spiking neurons is known as Liquid state machines.[5]
Long short term memory network[edit]
The Long short term memory (LSTM) network, developed by Hochreiter & Schmidhuber in 1997,[6] is an artificial neural net structure that unlike traditional RNNs doesn't have the problem of vanishing gradients (compare the section on training algorithms below). It works even when there are long delays, and it can handle signals that have a mix of low and high frequency components. LSTM RNN outperformed other methods in numerous applications such as language learning[7] and connected handwriting recognition.[8]
Bi-directional RNN[edit]
Invented by Schuster & Paliwal in 1997,[9] bi-directional RNN or BRNN use a finite sequence to predict or label each element of the sequence based on both the past and the future context of the element. This is done by adding the outputs of two RNN, one processing the sequence from left to right, the other one from right to left. The combined outputs are the predictions of the teacher-given target signals. This technique proved to be especially useful when combined with LSTM RNN.[10]
Continuous-time RNN[edit]
A continuous time recurrent neural network (CTRNN) is a dynamical systems model of biological neural networks. A CTRNN uses a system of ordinary differential equations to model the effects on a neuron of the incoming spike train. CTRNNs are more computationally efficient than directly simulating every spike in a network as they do not model neural activations at this level of detail[citation needed] .
For a neuron 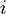 in the network with action potential
in the network with action potential 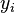 the rate of change of activation is given by:
the rate of change of activation is given by:

Where:
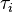 : Time constant of postsynaptic node
: Time constant of postsynaptic node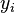 : Activation of postsynaptic node
: Activation of postsynaptic node : Rate of change of activation of postsynaptic node
: Rate of change of activation of postsynaptic node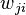 : Weight of connection from pre to postsynaptic node
: Weight of connection from pre to postsynaptic node : Sigmoid of x e.g.
: Sigmoid of x e.g. 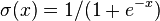 .
.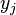 : Activation of presynaptic node
: Activation of presynaptic node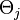 : Bias of presynaptic node
: Bias of presynaptic node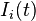 : Input (if any) to node
: Input (if any) to node
CTRNNs have frequently been applied in the field of evolutionary robotics, where they have been used to address, for example, vision,[11] co-operation[12] and minimally cognitive behaviour.[13]
Hierarchical RNN[edit]
There are many instances of hierarchical RNN whose elements are connected in various ways to decompose hierarchical behavior into useful subprograms.[14][15]
Recurrent multilayer perceptron[edit]
Generally, a Recurrent Multi-Layer Perceptron (RMLP) consists of a series of cascaded subnetworks, each of which consists of multiple layers of nodes. Each of these subnetworks is entirely feed-forward except for the last layer, which can have feedback connections among itself. Each of these subnets is connected only by feed forward connections.[16]
Second Order Recurrent Neural Network[edit]
Second order RNNs use higher order weights 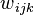 instead of the standard
instead of the standard  weights, and inputs and states can be a product. This allows a direct mapping to a finite state machine both in training and in representation.[citation needed] Long short term memory is an example of this.
weights, and inputs and states can be a product. This allows a direct mapping to a finite state machine both in training and in representation.[citation needed] Long short term memory is an example of this.
Pollack’s sequential cascaded networks[edit]
Training[edit]
Gradient descent[edit]
To minimize total error, gradient descent can be used to change each weight in proportion to its derivative with respect to the error, provided the non-linear activation functions are differentiable. Various methods for doing so were developed in the 1980s and early 1990s by Paul Werbos, Ronald J. Williams, Tony Robinson, Jürgen Schmidhuber, Sepp Hochreiter, Barak Pearlmutter, and others.
The standard method is called "backpropagation through time" or BPTT, and is a generalization of back-propagation for feed-forward networks,[17][18] and like that method, is an instance of Automatic differentiation in the reverse accumulation mode orPontryagin's minimum principle. A more computationally expensive online variant is called "Real-Time Recurrent Learning" or RTRL,[19][20] which is an instance of Automatic differentiation in the forward accumulation mode with stacked tangent vectors. Unlike BPTT this algorithm is local in time but not local in space.[21][22]
There also is an online hybrid between BPTT and RTRL with intermediate complexity,[23][24] and there are variants for continuous time.[25] A major problem with gradient descent for standard RNN architectures is that error gradients vanish exponentially quickly with the size of the time lag between important events.[26] [27] The Long short term memory architecture together with a BPTT/RTRL hybrid learning method was introduced in an attempt to overcome these problems.[6]
Global optimization methods[edit]
Training the weights in a neural network can be modeled as a non-linear global optimization problem. A target function can be formed to evaluate the fitness or error of a particular weight vector as follows: First, the weights in the network are set according to the weight vector. Next, the network is evaluated against the training sequence. Typically, the sum-squared-difference between the predictions and the target values specified in the training sequence is used to represent the error of the current weight vector. Arbitrary global optimization techniques may then be used to minimize this target function.
The most common global optimization method for training RNNs is genetic algorithms, especially in unstructured networks.[28][29][30]
Initially, the genetic algorithm is encoded with the neural network weights in a predefined manner where one gene in the chromosome represents one weight link, henceforth; the whole network is represented as a single chromosome. The fitness function is evaluated as follows: 1) each weight encoded in the chromosome is assigned to the respective weight link of the network ; 2) the training set of examples is then presented to the network which propagates the input signals forward ; 3) the mean-squared-error is returned to the fitness function ; 4) this function will then drive the genetic selection process.
There are many chromosomes that make up the population; therefore, many different neural networks are evolved until a stopping criterion is satisfied. A common stopping scheme is: 1) when the neural network has learnt a certain percentage of the training data or 2) when the minimum value of the mean-squared-error is satisfied or 3) when the maximum number of training generations has been reached. The stopping criterion is evaluated by the fitness function as it gets the reciprocal of the mean-squared-error from each neural network during training. Therefore, the goal of the genetic algorithm is to maximize the fitness function, hence, reduce the mean-squared-error.
Other global (and/or evolutionary) optimization techniques may be used to seek a good set of weights such as Simulated annealing or Particle swarm optimization.
Related fields[edit]
RNNs may behave chaotically. In such cases, dynamical systems theory may be used for analysis.
Issues with recurrent neural networks[edit]
Most RNNs have had scaling issues. In particular, RNNs cannot be easily trained for large numbers of neuron units nor for large numbers of inputs units. Successful training has been mostly in time series problems with few inputs.
References[edit]
- Jump up^ A. Graves, M. Liwicki, S. Fernandez, R. Bertolami, H. Bunke, J. Schmidhuber. A Novel Connectionist System for Improved Unconstrained Handwriting Recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 31, no. 5, 2009.
- Jump up^ Rául Rojas (1996). Neural networks: a systematic introduction. Springer. p. 336. ISBN 978-3-540-60505-8.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Cruse, Holk; Neural Networks as Cybernetic Systems, 2nd and revised edition
- Jump up^ H. Jaeger. Harnessing nonlinearity: Predicting chaotic systems and saving energy in wireless communication. Science, 304:78–80, 2004.
- Jump up^ W. Maass, T. Natschläger, and H. Markram. A fresh look at real-time computation in generic recurrent neural circuits. Technical report, Institute for Theoretical Computer Science, TU Graz, 2002.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Hochreiter, Sepp; and Schmidhuber, Jürgen; Long Short-Term Memory, Neural Computation, 9(8):1735–1780, 1997
- Jump up^ Gers, Felix A.; and Schmidhuber, Jürgen; LSTM Recurrent Networks Learn Simple Context Free and Context Sensitive Languages, IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 12(6):1333–1340, 2001
- Jump up^ Graves, Alex; and Schmidhuber, Jürgen; Offline Handwriting Recognition with Multidimensional Recurrent Neural Networks, in Bengio, Yoshua; Schuurmans, Dale; Lafferty, John; Williams, Chris K. I.; and Culotta, Aron (eds.), Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 22 (NIPS'22), December 7th–10th, 2009, Vancouver, BC, Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS) Foundation, 2009, pp. 545–552
- Jump up^ Bidirectional recurrent neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 45:2673–81, November 1997.
- Jump up^ A. Graves and J. Schmidhuber. Framewise phoneme classification with bidirectional LSTM and other neural network architectures. Neural Networks, 18:602–610, 2005.
- Jump up^ Harvey, Inman; Husbands, P. and Cliff, D. (1994). "Seeing the light: Artificial evolution, real vision". Proceedings of the third international conference on Simulation of adaptive behavior: from animals to animats 3: 392–401.
- Jump up^ Quinn, Matthew (2001). "Evolving communication without dedicated communication channels". Advances in Artificial Life: 357–366.
- Jump up^ Beer, R.D. (1997). "The dynamics of adaptive behavior: A research program". Robotics and Autonomous Systems: 257–289.
- Jump up^ J. Schmidhuber. Learning complex, extended sequences using the principle of history compression. Neural Computation, 4(2):234-242, 1992
- Jump up^ Dynamic Representation of Movement Primitives in an Evolved Recurrent Neural Network
- Jump up^ http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.45.3527
- Jump up^ P. J. Werbos. Generalization of backpropagation with application to a recurrent gas market model. Neural Networks, 1, 1988.
- Jump up^ David E. Rumelhart; Geoffrey E. Hinton; Ronald J. Williams. Learning Internal Representations by Error Propagation.
- Jump up^ A. J. Robinson and F. Fallside. The utility driven dynamic error propagation network. Technical Report CUED/F-INFENG/TR.1, Cambridge University Engineering Department, 1987.
- Jump up^ R. J. Williams and D. Zipser. Gradient-based learning algorithms for recurrent networks and their computational complexity. In Back-propagation: Theory, Architectures and Applications. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum, 1994.
- Jump up^ J. Schmidhuber. A local learning algorithm for dynamic feedforward and recurrent networks. Connection Science, 1(4):403–412, 1989.
- Jump up^ Neural and Adaptive Systems: Fundamentals through Simulation. J.C. Principe, N.R. Euliano, W.C. Lefebvre
- Jump up^ J. Schmidhuber. A fixed size storage O(n3) time complexity learning algorithm for fully recurrent continually running networks. Neural Computation, 4(2):243–248, 1992.
- Jump up^ R. J. Williams. Complexity of exact gradient computation algorithms for recurrent neural networks. Technical Report Technical Report NU-CCS-89-27, Boston: Northeastern University, College of Computer Science, 1989.
- Jump up^ B. A. Pearlmutter. Learning state space trajectories in recurrent neural networks. Neural Computation, 1(2):263–269, 1989.
- Jump up^ S. Hochreiter. Untersuchungen zu dynamischen neuronalen Netzen. Diploma thesis, Institut f. Informatik, Technische Univ. Munich, 1991.
- Jump up^ S. Hochreiter, Y. Bengio, P. Frasconi, and J. Schmidhuber. Gradient flow in recurrent nets: the difficulty of learning long-term dependencies. In S. C. Kremer and J. F. Kolen, editors, A Field Guide to Dynamical Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE Press, 2001.
- Jump up^ F. J. Gomez and R. Miikkulainen. Solving non-Markovian control tasks with neuroevolution. Proc. IJCAI 99, Denver, CO, 1999. Morgan Kaufmann.
- Jump up^ Applying Genetic Algorithms to Recurrent Neural Networks for Learning Network Parameters and Architecture. O. Syed, Y. Takefuji
- Jump up^ F. Gomez, J. Schmidhuber, R. Miikkulainen. Accelerated Neural Evolution through Cooperatively Coevolved Synapses. Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR), 9:937-965, 2008.
- Mandic, D. & Chambers, J. (2001). Recurrent Neural Networks for Prediction: Learning Algorithms, Architectures and Stability. Wiley. ISBN 0-471-49517-4.
- Elman, J.L. (1990). "Finding Structure in Time". Cognitive Science 14 (2): 179–211. doi:10.1016/0364-0213(90)90002-E.
External links[edit]