C. Basic determinants
Basic causes are identified as: institutions (formal and informal), political (structure, function and polices of the state) and ideological (religion, culture, tradition and beliefs) framework, economic structure and resources, environment, technology and people.
Those causes at below underlying caucuses are called basic causes. Basic causes in Figure 7 (the conceptual framework) are identified as: institutions (formal and informal), political (structure, function and polices of the state) and ideological (religion, culture, tradition and beliefs) framework, economic structure and resources, environment, technology and people.
Figure 7: Conceptual framework of basic, underlying and immediate causes of child under nutrition
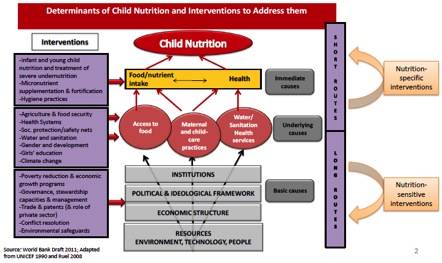
Because these causes are so wide ranging and context specific, it is difficult to make any predictive statements with the strength that could be made about the immediate causes.
Figure 7 proposes some of the major interventions that could have an impact on the basic causes. The basic causes of under nutrition in society also relate to both the historical background of the society and factors external to the society.
The pathways between basic causes and child under nutrition are however long and difficult to detect. Yet they are very important. The section on Indirect Nutrition Interventions describes the interventions and discusses where evidence is available as to the strength and nature of basic causes.