Boltzmann-Schuetz hypothesis
Boltzmann and Schuetz claimed that in a universe that is near thermal equilibrium, and given sufficient time, there will be regions where there is a temporary deviation into a low entropy state, from which it will trend back to equilibrium. Anthropic selection accounts for us being in such a region.
Boltzmann suggested this explanation in a letter to
Nature in 1895 - he attributes the idea 'to my old assistant Dr Schuetz'. The basic idea is depicted in the following diagram. The downward spikes represent low-entropy occurrences, with the system in the high entropy state most of the time. We are presumed to be at some position like A or B - the slope doesn't matter (case C is discussed elsewhere).
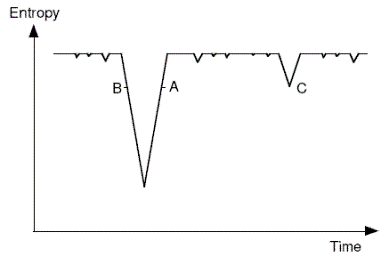
Note that in the passage cited below Boltzmann presumes that the thermodynamic arrow determines the psychological arrow of time. This issue is explored elsewhere in the map (follow cross-link).